See What Great Green Macaw Tricks The Celebs Are Making Use Of
페이지 정보
Writer Marcel 작성일25-01-05 12:09 count6 Reply0본문
| Subject | See What Great Green Macaw Tricks The Celebs Are Making Use Of | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Writer | Marcel Mindy catalina macaw & Marcel Services | Tel | 208115291 |
| host | grade | ||
| Mobile | 208115291 | marcel.harpur@mail.ru | |
| etc | |||
Information Regarding the Great Green Macaw
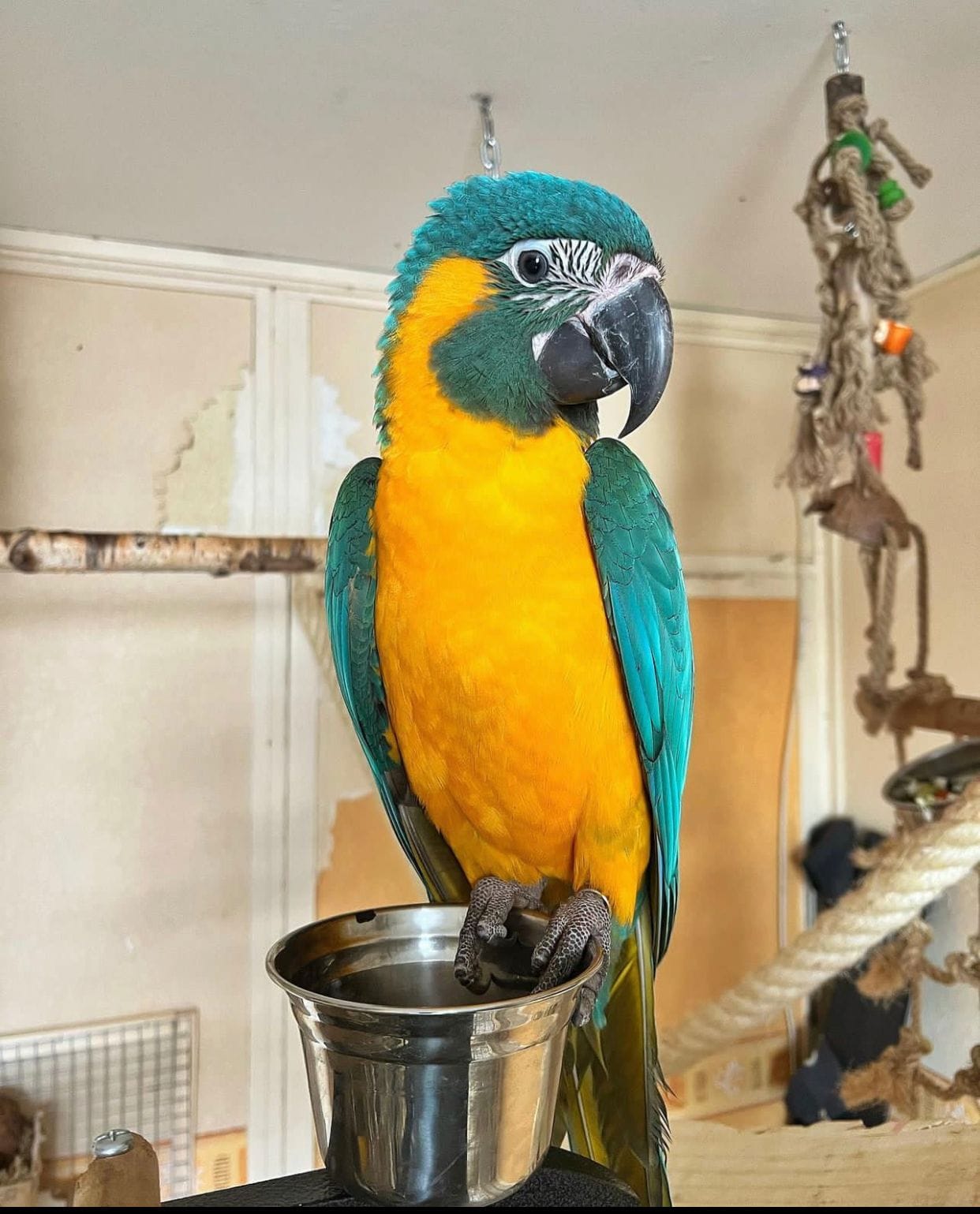 Great green macaws, despite their vibrant beauty, are threatened. They are among birds that are endangered and their habitat is being threatened due to the loss of forest.
Great green macaws, despite their vibrant beauty, are threatened. They are among birds that are endangered and their habitat is being threatened due to the loss of forest.
MRN is working to preserve their natural habitat and to create corridors between protected areas. MRN also partners with local communities to educate on the importance of this species.
Habitat
The great green macaw, despite being one of the most beautiful and intelligent birds in the world, has faced a number threats in the last few decades. BirdLife International has listed this species as critically endangered. The distribution and numbers have been greatly reduced due to habitat loss, unsustainable logging, and conversion to agriculture. Farmers are also known to shoot these beautiful birds as they are viewed by them as pests to crops and they also capture them for the pet trade.
In the wild, these beautiful birds occupy humid lowland forests as well as the edges of forests. They feed primarily on mountain almond trees (Dipterix panamensis) and nest in tree cavities. They are renowned for their highly sociable behavior and living in families during the off-season of breeding.
Their tail feathers and wing feathers are long, sharply pointed to ensure efficient flight in the forest canopy. Their beaks are large and robust, allowing them open up the tough shells of nuts, seeds and bark. They also love to eat flowers, roots and fruits. The great green macaw is a vocal species that makes a variety of calls to communicate with other members of their group and with potential friends. Their calls can be heard as screeches, whistles and squawks.
They play a crucial role in their ecosystems by dispersing seeds. The presence of this species in the wild helps to improve the health and diversity rainforest habitats. They are a vital part of the food web, attracting animals such as monkeys and insects which help spread the seeds of trees and plants.
Fortunately Non-profit organizations are working to protect the habitat of these magnificent birds. They are buying land to establish reserves and working with local communities to promote sustainable livelihoods. They are implementing conservation practices to reduce contact between macaws and humans and providing educational opportunities so people can learn about this beautiful and magnificent bird. This magnificent creature in its natural environment is truly a once-in-a-lifetime experience.
Diet
The great green macaw; https://mozillabd.science/wiki/Are_Macaw_Parrot_Cost_Really_As_Vital_As_Everyone_Says, is an amazing bird that is found in the rainforests of Central and South America. They are a pair or small groups, and spend the majority of their time high in the trees eating fruits, seeds, and nuts. Their strong beaks are used to crack open the hard shells. They are, therefore, important seeds dispersers and help maintain healthy forests. They also play a role in the ecosystem by providing food for other endangered species like the Scarlet Macaw and Yellow-naped Amazon.
The large parrot is mostly green with splashes of bright red on the forehead, cheeks and lower back. The tops of their heads why are the glaceous macaw and hyancith macaw so alike bare and they have an extended beak with an incredibly curvature. The curve is an adaptation that allows them to break open the hard shells of seeds, nuts and other nuts.
In the wild they consume a variety of things like seeds, bark and roots and also bulbs, flowers and fruits. They are known to particularly enjoy the fruit of the mountain almond tree (Almendra guayaquilensis). They also visit clay-licks, where birds lick clay in the belief that it is beneficial for their health.
Great green macaws are threatened in the wild due to habitat loss which means that they can't obtain enough food to sustain themselves. They are also seized illegally for pet trade.
The good news is that numerous organizations are working to safeguard this magnificent bird and ensure it has a safe home in the wild. World Land Trust, as an example, has a relationship with reserves such as the Rio Canande Reserve, in Ecuador, where artificial macaws nests have been set up.
For those keeping the birds as pets it is essential to give them plenty of space and food that is similar to the kind they would eat in the wild. They should be given lots of fresh fruits and vegetables and include those high in vitamins such as sweet potatoes, bananas carrots and oranges. It's also a good idea to let them out of their cage for 2-3 hours each day to play, stretch their wings, around and play. This will help them stay healthy and happy.
Nesting
The great green macaw lays its eggs in a crevice or cavity in a tree usually in the trunk of a mountain almendro (Dipteryx panamensis) or tit o (Sacoglottis trichogyna). They also use other trees, such as beach almond (Dipteryx oleifera) and the cativo (Prioria copaifera) and caobilla (Carapa nicaraguensis). A pair of birds can lay up to two eggs. The incubation time is about 28 days. The chicks leave the nest after they are fledged.
The biggest threat to the species is human-caused habitat loss, specifically through logging and agricultural. In Costa Rica, where the great green macaw is listed as endangered, there has been a significant decline in the population due to deforestation, especially since the 1980s. There is an abundance of enthusiasm for conservation efforts to save the species, but the task is enormous.
Education is crucial, along with habitat preservation. Outreach programs in schools and communities aid people to realize the importance of the bird and encourage people to be involved in conservation efforts. Eco-tourism is a different tool that provides economic incentives for people to protect great green buy macaw habitat.
Research has revealed that there aren't enough breeding pairs to sustain and grow the population. It is essential to establish protected areas and reserve corridors for the birds to find suitable partners. Conservation efforts include captive breeding and the creation of artificial nests that lower the risk of predation.
Poaching is a major issue for the great green macaw particularly in Central America where the birds are often killed because of their attractive markings or are viewed as agricultural pests and shot. In Ecuador, WLT supporter ProBosque is working with local communities to safeguard the species at the Rio Canande Reserve and Cerro Blanco Woodland Reserve. The project is studying the effects of artificial nesting in this vulnerable region. The findings will be the basis for the development of new, better designs for nests that will reduce the chance of predation by a variety of animals. These improvements are a major improvement in the fight to save this magnificent bird.
Breeding Season
The breeding season of the great green macaw runs between January and August with peaking in February and May. In this period the female will select a nesting site within the forest canopy, usually one of the species Dipteryx oleifera. The female will lay between 2 and 3 eggs, which will be incubated between 26 and 28 days. Both parents will feed the chicks. The average first-year survival is 65percent.
Due to the heightened risks of predation and the unstable habitat, it is difficult for the great green macaw to maintain an unchanging population. Conservationists have created artificial nests that are placed in safe and secure trees to help combat this. These nests protect the young against predators and weather conditions. They also offer a way for humans to monitor the success of the birds and their breeding.
Great green macaws are usually seen in pairs, but they can be seen in small groups of 10 to 15 individuals too. They are found in the lowland tropical rainforest that extends from eastern Honduras to northwestern Colombia and western Ecuador. The birds are found primarily in the canopy of the forest, but they also frequent foothill forests. They feed on seeds and fruits and sometimes hard-shelled nuts shells.
Many non-profit organizations why are the glaceous macaw and hyancith macaw so alike working towards protecting the natural habitat of the great green macaw. They purchase land and work with local communities to promote sustainable farming practices as well as alternative sources of income. They also monitor the macaws in order to identify threats and mitigate those threats.
Being able to see the magnificent green macaw in its natural surroundings is an unforgettable experience for many tourists visiting Costa Rica. Birdwatching is provided by a variety of eco-lodges, tour operators and eco-lodges. Tourists are given the chance to see these beautiful bird species while learning about their habitats.
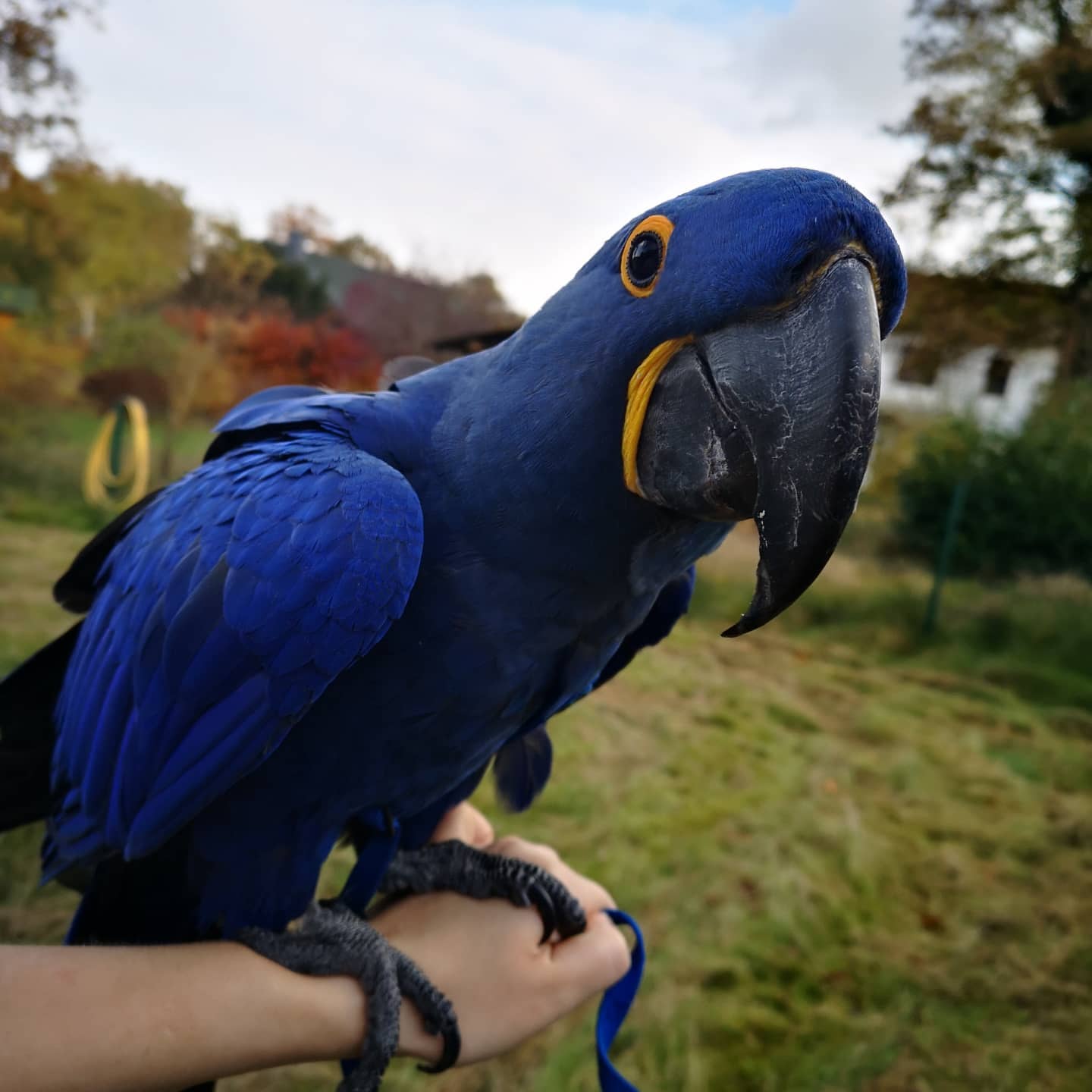 With the threat of habitat loss from mining and logging, the population of the great green macaw is decreasing. Conservationists are making a difference through the establishment of protected areas and making sure that the macaw has access to routes between these areas. They are also establishing breeding programs and encouraging community involvement to help save the macaw and other species.
With the threat of habitat loss from mining and logging, the population of the great green macaw is decreasing. Conservationists are making a difference through the establishment of protected areas and making sure that the macaw has access to routes between these areas. They are also establishing breeding programs and encouraging community involvement to help save the macaw and other species.
 Great green macaws, despite their vibrant beauty, are threatened. They are among birds that are endangered and their habitat is being threatened due to the loss of forest.
Great green macaws, despite their vibrant beauty, are threatened. They are among birds that are endangered and their habitat is being threatened due to the loss of forest.MRN is working to preserve their natural habitat and to create corridors between protected areas. MRN also partners with local communities to educate on the importance of this species.
Habitat
The great green macaw, despite being one of the most beautiful and intelligent birds in the world, has faced a number threats in the last few decades. BirdLife International has listed this species as critically endangered. The distribution and numbers have been greatly reduced due to habitat loss, unsustainable logging, and conversion to agriculture. Farmers are also known to shoot these beautiful birds as they are viewed by them as pests to crops and they also capture them for the pet trade.
In the wild, these beautiful birds occupy humid lowland forests as well as the edges of forests. They feed primarily on mountain almond trees (Dipterix panamensis) and nest in tree cavities. They are renowned for their highly sociable behavior and living in families during the off-season of breeding.
Their tail feathers and wing feathers are long, sharply pointed to ensure efficient flight in the forest canopy. Their beaks are large and robust, allowing them open up the tough shells of nuts, seeds and bark. They also love to eat flowers, roots and fruits. The great green macaw is a vocal species that makes a variety of calls to communicate with other members of their group and with potential friends. Their calls can be heard as screeches, whistles and squawks.
They play a crucial role in their ecosystems by dispersing seeds. The presence of this species in the wild helps to improve the health and diversity rainforest habitats. They are a vital part of the food web, attracting animals such as monkeys and insects which help spread the seeds of trees and plants.
Fortunately Non-profit organizations are working to protect the habitat of these magnificent birds. They are buying land to establish reserves and working with local communities to promote sustainable livelihoods. They are implementing conservation practices to reduce contact between macaws and humans and providing educational opportunities so people can learn about this beautiful and magnificent bird. This magnificent creature in its natural environment is truly a once-in-a-lifetime experience.
Diet
The great green macaw; https://mozillabd.science/wiki/Are_Macaw_Parrot_Cost_Really_As_Vital_As_Everyone_Says, is an amazing bird that is found in the rainforests of Central and South America. They are a pair or small groups, and spend the majority of their time high in the trees eating fruits, seeds, and nuts. Their strong beaks are used to crack open the hard shells. They are, therefore, important seeds dispersers and help maintain healthy forests. They also play a role in the ecosystem by providing food for other endangered species like the Scarlet Macaw and Yellow-naped Amazon.
The large parrot is mostly green with splashes of bright red on the forehead, cheeks and lower back. The tops of their heads why are the glaceous macaw and hyancith macaw so alike bare and they have an extended beak with an incredibly curvature. The curve is an adaptation that allows them to break open the hard shells of seeds, nuts and other nuts.
In the wild they consume a variety of things like seeds, bark and roots and also bulbs, flowers and fruits. They are known to particularly enjoy the fruit of the mountain almond tree (Almendra guayaquilensis). They also visit clay-licks, where birds lick clay in the belief that it is beneficial for their health.
Great green macaws are threatened in the wild due to habitat loss which means that they can't obtain enough food to sustain themselves. They are also seized illegally for pet trade.
The good news is that numerous organizations are working to safeguard this magnificent bird and ensure it has a safe home in the wild. World Land Trust, as an example, has a relationship with reserves such as the Rio Canande Reserve, in Ecuador, where artificial macaws nests have been set up.
For those keeping the birds as pets it is essential to give them plenty of space and food that is similar to the kind they would eat in the wild. They should be given lots of fresh fruits and vegetables and include those high in vitamins such as sweet potatoes, bananas carrots and oranges. It's also a good idea to let them out of their cage for 2-3 hours each day to play, stretch their wings, around and play. This will help them stay healthy and happy.
Nesting
The great green macaw lays its eggs in a crevice or cavity in a tree usually in the trunk of a mountain almendro (Dipteryx panamensis) or tit o (Sacoglottis trichogyna). They also use other trees, such as beach almond (Dipteryx oleifera) and the cativo (Prioria copaifera) and caobilla (Carapa nicaraguensis). A pair of birds can lay up to two eggs. The incubation time is about 28 days. The chicks leave the nest after they are fledged.
The biggest threat to the species is human-caused habitat loss, specifically through logging and agricultural. In Costa Rica, where the great green macaw is listed as endangered, there has been a significant decline in the population due to deforestation, especially since the 1980s. There is an abundance of enthusiasm for conservation efforts to save the species, but the task is enormous.
Education is crucial, along with habitat preservation. Outreach programs in schools and communities aid people to realize the importance of the bird and encourage people to be involved in conservation efforts. Eco-tourism is a different tool that provides economic incentives for people to protect great green buy macaw habitat.
Research has revealed that there aren't enough breeding pairs to sustain and grow the population. It is essential to establish protected areas and reserve corridors for the birds to find suitable partners. Conservation efforts include captive breeding and the creation of artificial nests that lower the risk of predation.
Poaching is a major issue for the great green macaw particularly in Central America where the birds are often killed because of their attractive markings or are viewed as agricultural pests and shot. In Ecuador, WLT supporter ProBosque is working with local communities to safeguard the species at the Rio Canande Reserve and Cerro Blanco Woodland Reserve. The project is studying the effects of artificial nesting in this vulnerable region. The findings will be the basis for the development of new, better designs for nests that will reduce the chance of predation by a variety of animals. These improvements are a major improvement in the fight to save this magnificent bird.
Breeding Season
The breeding season of the great green macaw runs between January and August with peaking in February and May. In this period the female will select a nesting site within the forest canopy, usually one of the species Dipteryx oleifera. The female will lay between 2 and 3 eggs, which will be incubated between 26 and 28 days. Both parents will feed the chicks. The average first-year survival is 65percent.
Due to the heightened risks of predation and the unstable habitat, it is difficult for the great green macaw to maintain an unchanging population. Conservationists have created artificial nests that are placed in safe and secure trees to help combat this. These nests protect the young against predators and weather conditions. They also offer a way for humans to monitor the success of the birds and their breeding.
Great green macaws are usually seen in pairs, but they can be seen in small groups of 10 to 15 individuals too. They are found in the lowland tropical rainforest that extends from eastern Honduras to northwestern Colombia and western Ecuador. The birds are found primarily in the canopy of the forest, but they also frequent foothill forests. They feed on seeds and fruits and sometimes hard-shelled nuts shells.
Many non-profit organizations why are the glaceous macaw and hyancith macaw so alike working towards protecting the natural habitat of the great green macaw. They purchase land and work with local communities to promote sustainable farming practices as well as alternative sources of income. They also monitor the macaws in order to identify threats and mitigate those threats.
Being able to see the magnificent green macaw in its natural surroundings is an unforgettable experience for many tourists visiting Costa Rica. Birdwatching is provided by a variety of eco-lodges, tour operators and eco-lodges. Tourists are given the chance to see these beautiful bird species while learning about their habitats.
 With the threat of habitat loss from mining and logging, the population of the great green macaw is decreasing. Conservationists are making a difference through the establishment of protected areas and making sure that the macaw has access to routes between these areas. They are also establishing breeding programs and encouraging community involvement to help save the macaw and other species.
With the threat of habitat loss from mining and logging, the population of the great green macaw is decreasing. Conservationists are making a difference through the establishment of protected areas and making sure that the macaw has access to routes between these areas. They are also establishing breeding programs and encouraging community involvement to help save the macaw and other species.
 JOIN
JOIN